Developed within the MODELAN project, the novel method has as one of its main keys the use of simulation tools, together with the detailed analysis of the metallurgical characteristics of the component and its manufacturing process.
Heat treatment of metallic components is a key step to consolidate material properties and achieve a more efficient manufacturing cycle. For its proper design, it is essential to know the final application of the parts and, consequently, the specifications that the component must meet, in the form of mechanical and microstructural properties. These aspects will define both the type of treatment to which the components must undergo (Normalization, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, Carburizing,…), as well as the precise conditions of said treatments which, although may be subject to specific manufacturing standards, also may present some flexibility in their selection or adjustment.
As explained by the expert in steel casting and special materials of AZTERLAN Fernando Santos, “the heat treatment of the parts must be designed not only seeking greater sustainability and efficiency in the process, but it is necessary to take into account that any mismatch in it (such as, for example, any possible deviation in application times or temperatures), it can have other negative side effects. It is necessary to take into account the starting point of the material, associated with the different manufacturing processes and conditions. Metallurgy plays a fundamental role and all these aspects determine the homogeneity of the chemical elements present and, in turn, the optimal thermal treatment.”
Thus, the methodology developed by the Technology Center proposes the establishment of a precise starting point at the microstructural and chemical level of the part, followed by a combination of material and process simulations that, in combination, allow the design and adjustment of the thermal treatment. optimal, taking into account the specific characteristics of the parts.
Among other aspects, the new methodology is based on the evaluation of aspects such as the geometry of the part, the segregations of the different chemical elements and the conditions of their diffusion during the forming and cooling processes of the components. Subsequently, with the support of simulation and prediction tools that address in a combined way aspects related to the process and the material, essential characteristics such as phase formation, chemical element segregations and some mechanical characteristics are evaluated. This extensive preliminary study “allows us to determine the most sustainable and appropriate heat treatment to achieve the specifications of the final product.”
The new methodology, branded after TREAT, can be used for all types of metal components obtained through transformation processes such as foundry, steelmaking, forging or stamping, which require subsequent heat treatment to meet certain specifications of the final product.
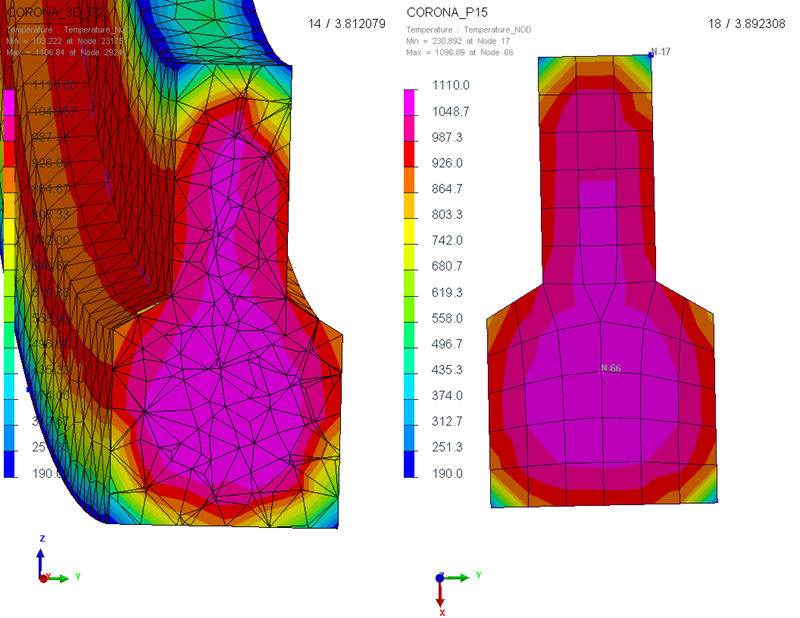
Example of modeling a temperature profile during the heat treatment of a specific geometry
The MODELAN project, participated by AZTERLAN, GHI, GUIVISA, EIPC, MIMTECH, RAZYA and SIDENOR, is financed by the HAZITEK program of the Basque Government.


